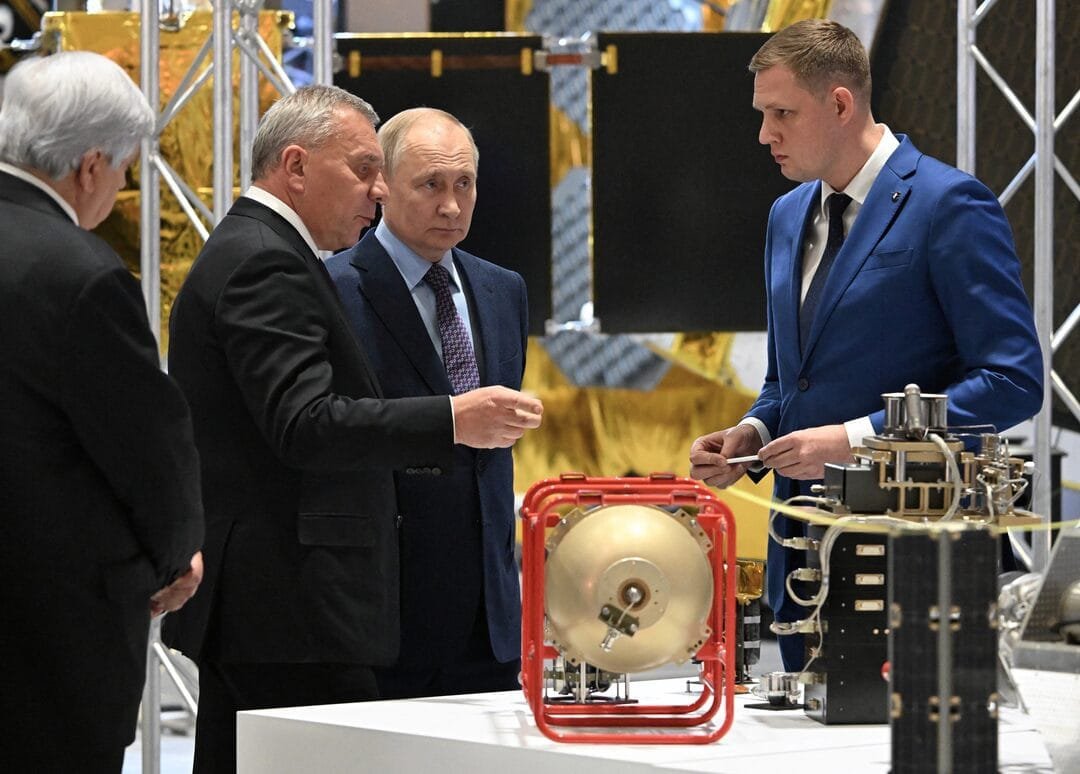
President Putin meets aerospace experts in Samara to push rocket engine development.
Preface Reviving Russia Space Ambitions
Russian President Vladimir Putin on 6 September called on Russian aerospace industry leaders in the southern Russian city of Samara to step up efforts to develop booster rocket engines, part of Russia’s age-old ambition to establish itself as a world leader in space technology. Putin, who has been in China and Russia’s Far Eastern port of Vladivostok for the past week, arrived in Samara where he met industry experts and visited the Kuznetsov Design Bureau aircraft engine manufacturing plant. The key points that Putin made during the visit not only reflect Russia’s space ambitions but also underline Russia’s strategy to become self-reliant through technological development despite Western sanctions.
A glorious tradition inherited from the Soviet Union
Russia space ambitions has inherited a glorious history in the field of space technology. The Soviet Union ushered in the space age by launching the world’s first artificial satellite Sputnik-1 on 4 October 1957. After this, on 12 April 1961, Yuri Gagarin became the first human to go into space. Also, these historic achievements established the Soviet Union and later Russia as a world leader in the field of space technology. And at the same time, Russia has achieved many important achievements while carrying forward this legacy, including significant contributions to the Soyuz spacecraft Salyut and Mir space stations and later the International Space Station (ISS).
Also, the current challenges and the impact of sanctions Although Russia has a glorious space history. But at present it is facing many serious challenges. The sanctions imposed by Western countries since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022 have severely affected the Russian space industry.
Emphasis on rocket engine development
Addressing aerospace industry leaders in Samara, Putin said that Russia remains a leading force in the development of the aerospace industry. He said, “It is important to constantly renew production capacity in terms of engines for booster rockets. And in doing so, we must not only meet our current and future needs but also actively advance in world markets and become successful competitors. This statement reflects Russia’s ambition. But in which it wants to meet not only domestic needs but also wants to make its presence felt in the global market. But due to these sanctions, Russia has been deprived of many opportunities for international cooperation and its access to technology has been limited. Despite these challenges, Putin stressed that Russia has succeeded in developing a range of engines for the energy sector even in the conditions of sanctions.
Mention of innovations in the energy sector Russia space ambitions
Putin in his speech mentioned Russian success in terms of engine development in the energy sector. But he said that in the conditions of sanctions from sanctions we managed to develop a range of innovative engines for energy. Also they are being actively used. Which is including in the context of gas transportation infrastructure. Putin called it an “extremely important topic”, especially The development of Russian gas exports to China includes the Power of Siberia 2 pipeline under discussion this week that will bring Russian gas to China.
Also, the key points of Putin’s Samara speech as well as the strategic importance that rocket engine development renewal of engine production capacity for booster rockets maintaining global competitiveness in the space industry innovation in the energy sector development of energy engines despite sanctions strengthening of gas export infrastructure as well as competing in the global market to become a successful competitor in the international market
The importance of the development of the PD-26 aircraft engine
Putin also pointed to the development of the PD-26 aircraft engine but saying that it will lead to the development of military transport and wide-body passenger aircraft. He also said that the development of this project will not only allow the modernization of military transport aircraft but will also open up possibilities for the creation of a new generation of wide-body civilian aircraft. But this comment is important because it reflects Russia’s goal in which it wants to become self-sufficient not only in the military but also in the civilian aviation sector.
Also, current rocket engine technology which Russia has been a leading country in the field of rocket engine technology for decades. Institutions such as Russia’s Kuznetsov Design Bureau have developed some of the world’s most reliable and powerful rocket engines. These include the RD-107 and RD-115 engines for Soyuz rockets, the RD-253 engine for Proton rockets, and the RD-191 engine for Angara rockets.
Future plans and innovative technologies on Russia space ambitions
Russia has ambitious plans for the future in the field of rocket engine technology. But these include innovative technologies such as plasma rocket engines. Also, researchers at Russia’s State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom have developed a prototype rocket engine.The Russian Federation has unveiled an electric plasma rocket engine. But which is capable of greatly increasing thrust and efficiency. Also, this propulsion breakthrough has been led by researchers at Rosatom. Which is the latest step in Moscow’s effort towards achieving technological mastery in nuclear and space technologies amid rising international tensions. According to a statement released by Rosatom, the new plasma engine prototype is based on a magnetic plasma accelerator. Can achieve a thrust of 6 Newton.
Benefits and prospects of plasma rocket engines
The possibilities of plasma rocket engines are extremely broad. Also, according to Alexei Voronov, First Deputy Director General for Science at Rosatom’s Troitsk-based Research Institute, a flight to Mars using conventional engines can take about a year on one side. But which is dangerous for astronauts due to cosmic radiation and radiation exposure. Also, Voronov said that with plasma engines, the travel time required for such a space mission can be reduced to one to two months. Which means that it will be possible to send an astronaut to Mars and bring him back. The plasma-powered engine operates by producing sequential pulses that achieve an average power of 300 kW, which far outstrips the capabilities of conventional chemical propulsion systems. In addition to reaching the speeds of conventional rockets, the plasma prototype reduces fuel consumption by at least ten times.
Russian engine technology offer to India
Russia has offered to supply India with the most technologically advanced warplane engines with no political strings attached to the deal. While the United States remains an unreliable partner as it attempts to play the ball game during the crisis, experts have told Sputnik India. Four military-industrial giants—France’s Safran, Britain’s Rolls-Royce, America’s General Electric and Russia’s UEC—are competing for a multi-billion dollar contract to supply advanced jet engines to India. Russia’s United Engine Corporation (UEC) is now able to not only remanufacture engines it previously produced. It can also modify them to enhance their tactical and technical characteristics, and is developing entirely new engines. This includes turboprop turbojet engines and even rocket engines.
India’s current requirements and the importance of the Russian proposal
India is in dire need of a state-of-the-art fighter jet engine, especially for its Tejas Mark-2 and Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft, the country’s first 5.5-generation fighter aircraft, reiterated retired Group Captain Uttam Kumar Debnath. India is also looking at an engine in the 110 kilo-newton+ range to power its indigenous Tejas fighters as well as the future AMCA, something that not many countries can provide. Yet Russia, the US, the UK and France are among the four sovereign states that have expressed a desire to partner with India. And in fact engines of this type have been offered by GE of the US. But the reliability and continuity of supply of these vital military systems is extremely doubtful as India has seen so far.
Russia’s Current Position and Future Plans
Russia remains an important player in the global space industry. But its position is facing challenges. Russia’s participation in the International Space Station is declining. It is focusing on the development of its own Russian Orbital Service Station (ROSS). However, sanctions and costs associated with the ongoing war on Ukraine have significantly affected Moscow’s space budget. And this has further delayed rocket and satellite development, meaning that plans to launch the first module of ROSS by 2027 will likely be postponed. New opportunities for international cooperation Despite these challenges, Russia has sought new opportunities for international cooperation. Relations with India are one of these important opportunities. Relations with China have also strengthened, as evidenced by discussions on the Power of Siberia 2 pipeline.
Conclusion: Russia space ambitions
Russian President Vladimir Putin’s call on the Russian aerospace industry to develop rocket engines reflects the country’s space ambitions and desire to achieve technological self-reliance despite Western sanctions. At the same time, Russia’s aerospace industry is balancing historical achievements and current challenges while developing innovative technologies such as plasma propulsion. Cooperation with Russia offers significant opportunities for India, especially in the defense and aerospace sectors. Russia’s willingness technology transfer and joint production offers can help enhance India’s strategic autonomy and technological capabilities. But India must carefully balance its international relationships and ensure that such cooperation serves its long-term interests.